Outdated or illegitimate software is like open doors for malicious users. The recent discovery by Kaspersky proves this once again. The global cybersecurity company today unveils a sustained campaign targeting users of Internet Explorer in the Asia Pacific region.
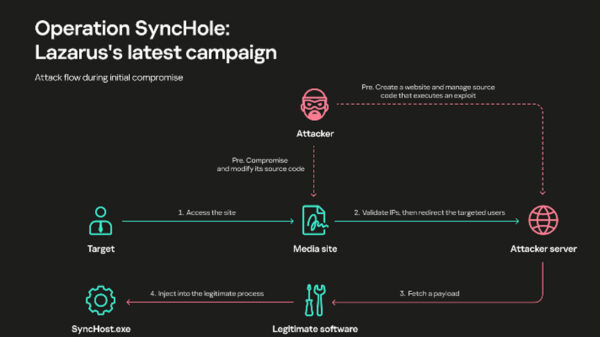
According to the fresh data from Kaspersky Security Network (KSN), an exploit kit dubbed as “Magnitude EK” has been actively evolving and trying to infect users in South Korea, Taiwan, and Hong Kong with new exploits.
“Magnitude EK is one of the longest-standing exploit kits. It was on offer in underground forums from 2013 and later became a private exploit kit. As well as a change of actors, the exploit kit has switched its focus to deliver ransomware to users from specific Asia Pacific (APAC) countries via malvertising. Our statistic shows that this campaign continues to target APAC countries to this day and during the year in question Magnitude EK always used its own ransomware as a final payload,” writes Boris Larin, security researcher at Kaspersky.
Exploits are typically distributed in packs containing multiple exploits for different vulnerabilities. Exploit kit, also known as exploit pack, is used to identify software installed on a victim’s computer, match it against the list of exploits in the pack and deploy the appropriate exploit if one of the applications installed is vulnerable.
Meanwhile, malvertising refers to the use of online ads to distribute malicious programs. Cybercriminals embed a special script in a banner or redirect users who click on an ad to a special page containing code for downloading malware. Special methods are used to bypass large ad network filters and place malicious content on trusted sites. In some cases, visitors do not even need to click on a fake ad—the code executes when the ad is displayed.
Kaspersky’s close monitoring also showed that Magnitude EK is actively maintained and undergoes continuous development. In February this year, it has switched to an exploit for the more recent vulnerability CVE-2019-1367 in Internet Explorer (originally discovered as an exploited zero-day in the wild).
In addition, the campaign’s older ransomware versions used to check hardcoded language IDs which include languages in Hong Kong, People’s Republic of China, Singapore, Taiwan, South Korea, Brunei Darussalam, and Malaysia. In newer versions, the check for the language ID was removed.
“As of last month, there is still a small percentage of online users in APAC browsing the web through Internet Explorer as it has remained the default web browser for Windows 7/8/8.1. Using obsolete software which will not receive security updates and vulnerability patches is synonymous to welcoming cybercriminals with open arms.Three years after the infamous Wannacry attack, businesses and individuals should now be more vigilant against ransomware and other types of attacks. All possible entry points in your systems and devices should be addressed as soon as possible,” comments Stephan Neumeier, managing director for Asia Pacific at Kaspersky.
Kaspersky recommends the following to keep devices and data safe:
- Pay careful attention to the websites you are visiting. Do not visit dubious sites and avoid clicking random ads.
- Do not use outdated versions of operating systems and other software. Make sure that you install any software updates in a timely fashion.
- Be critical of e-mail attachments, including ones that are sent from acquaintances. If a friend suddenly sends you an essay that you did not ask for, that is reason for suspicion.
- Pay attention to the extensions of the files that you are downloading. If you downloaded an EXE file instead of a document, do not open it.
- Use a reliable computer security solution